How to Mix and Hydrate Xanthan Gum
Xanthan Gum (E415 in Europe) is commonly used for its ability to thicken and stabilize emulsions and suspensions. When dispersed in water, it forms a gel-like structure that exhibits shear-thinning properties, meaning its viscosity decreases when subjected to shear stress (such as stirring, mixing, or pumping) but increases again when the stress is removed. This makes it ideal for applications like sauces, salad dressings, and shampoos, where it ensures a thick, stable consistency at rest while allowing for smooth flow when poured or applied. It is often combined with other rheology modifiers, such as guar gum, to further enhance its thickening and stabilizing effects.
Xanthan gum is widely used across industries, including food, cosmetics, and pharmaceuticals. To learn more about xanthan gum in chemical applications, check out our detailed application report.
Xanthan Gum Mixing Methods
Xanthan gum can be mixed into hot or cold liquids and many grades of gum are available. Because it has a strong tendency to form lumps when added to water, different dispersion and hydration techniques are used depending on production scale, formulation requirements, and other ingredients present. These can include:
- Gradual addition into an agitated vessel: The powder is slowly introduced into the vortex, helping to minimize clumping. Once dispersed, mixing continues to ensure full hydration.
- Premixing with dry ingredients: Blending with other powdered ingredients such as sugars separates the xanthan gum particles, helping reduce the risk of agglomeration.
- Using an oil or other liquid carrier: Initial dispersion in non-aqueous liquids such as glycerin or oils, followed by incorporation into the aqueous phase for hydration.
Common Problems When Mixing Xanthan Gum
As with most gums and thickeners, dispersing xanthan gum with conventional agitators can lead to several processing challenges:
Powder Dispersion & Agglomeration:
- Agglomerates can easily form, even when the methods outlined above are taken to reduce the risk. Agitators do not produce sufficient shear to rapidly break these down.
- Once viscosity increase has started, agitation of the solution and therefore powder dispersion becomes increasingly difficult.
Yield & Efficiency Challenges:
- Traditional methods often fail to achieve the full yield of xanthan gum’s thickening potential.
- Due to this shortfall in yield, many formulations compensate by adding surplus xanthan gum, which increases raw material costs.
- Long mixing times are required for full dispersion and hydration, but prolonged agitation can weaken the gel structure and diminish its functionality.
- Premixing xanthan gum with dry powders or non-aqueous liquids adds extra processing steps, increasing both time and cost.
Quality Control Issues:
- If xanthan gum is not fully hydrated during mixing, leftover particles may gradually absorb liquid over time, leading to unpredictable viscosity changes during storage or subsequent processing.
- It is not possible to create high percentage gum solutions with traditional methods. Solutions of this type may be required in certain applications where water is limited in the formulation.
The High-Speed Mixing Solution
A Silverson mixer can produce an agglomerate-free dispersion and fully hydrate xanthan gum in a fraction of the time taken by conventional methods. For in-tank applications, the Silverson Ultramix provides optimal performance.
The process works as follows:

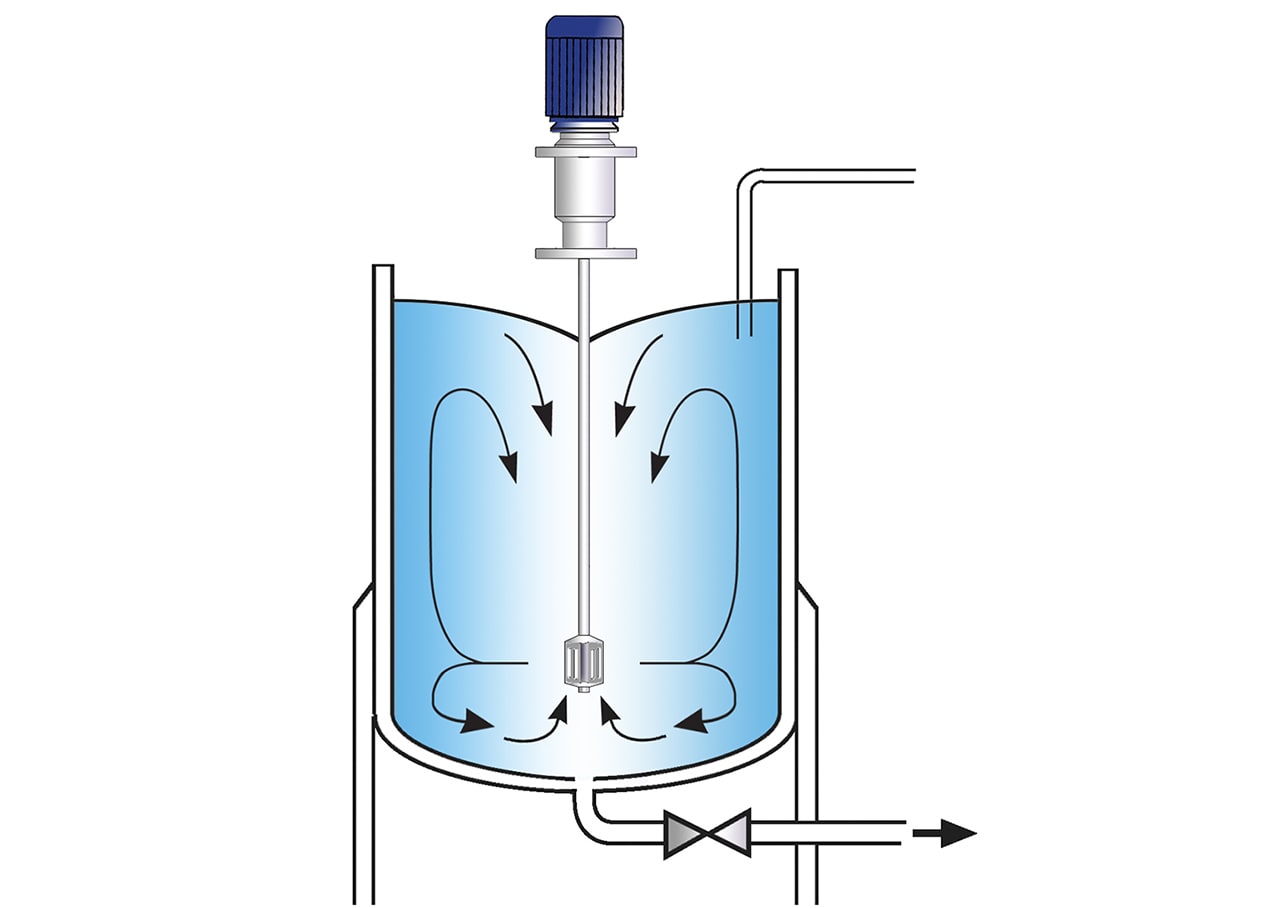
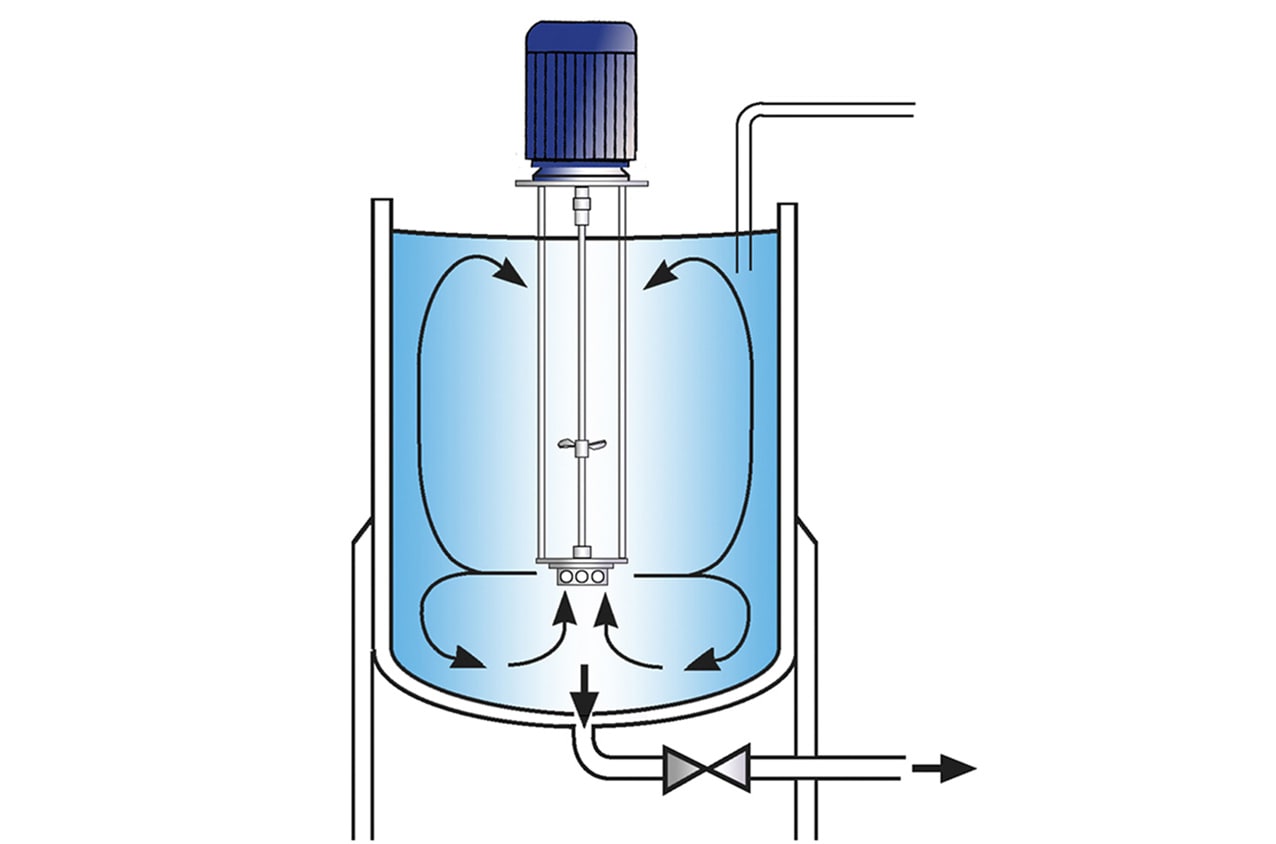
Stage 1
The vessel is charged with liquid and the mixer is started. The xanthan gum is added to the water as rapidly as possible. The high-speed rotation of the single-piece Ultramix workhead creates a powerful vortex, drawing the powder and liquid down into the workhead.

Stage 2
The materials are then forced through the slots in the side of the workhead and projected back into the body of the mix. Any agglomerates are broken down as they pass through the slots.

Stage 3
The vigorous movement in the vessel created by the Ultramix ensures that in a short mixing cycle all the material passes many times through the workhead, progressively reducing the particle size and exposing an increasing surface area to the surrounding liquid. This rapidly completes hydration.
-
Stage 1

Stage 1
The vessel is charged with liquid and the mixer is started. The xanthan gum is added to the water as rapidly as possible. The high-speed rotation of the single-piece Ultramix workhead creates a powerful vortex, drawing the powder and liquid down into the workhead.
-
Stage 2

Stage 2
The materials are then forced through the slots in the side of the workhead and projected back into the body of the mix. Any agglomerates are broken down as they pass through the slots.
-
Stage 3

Stage 3
The vigorous movement in the vessel created by the Ultramix ensures that in a short mixing cycle all the material passes many times through the workhead, progressively reducing the particle size and exposing an increasing surface area to the surrounding liquid. This rapidly completes hydration.
Advantages of Silverson Mixers
- Maximized yield and efficiency: Achieves full functionality with less xanthan gum, reducing raw material costs.
- Smooth, agglomerate-free dispersion: Ensures a uniform mix without clumps.
- Effectively eliminates operator error: Streamlined process reduces variability.
- Faster mixing times: Hydrates xanthan gum in a fraction of the time compared to conventional methods.
- Consistent quality and repeatability: Delivers reliable results batch after batch.
- No need for premixing: Eliminates the extra step of blending xanthan gum with other powders or non-aqueous liquids before hydration.
Silverson offers a range of mixers for this application. The ideal model depends on factors such as batch size, final product viscosity, xanthan gum concentration, and gum grade. Options include:
Silverson Ultramix
- Ultra-sanitary CIP (Clean-in-Place) design for hygienic applications.
- Generates strong in-tank movement for thorough mixing.
- Rapidly incorporates large amounts of powders into liquids.
- Ideal for higher viscosity mixes.
- Low-maintenance, robust design.
High Shear Batch Mixers
- Suitable for batches of up to 400 US gallons.
- Can be mounted on mobile floor stands for easy repositioning.
- Easily transferable between multiple vessels.
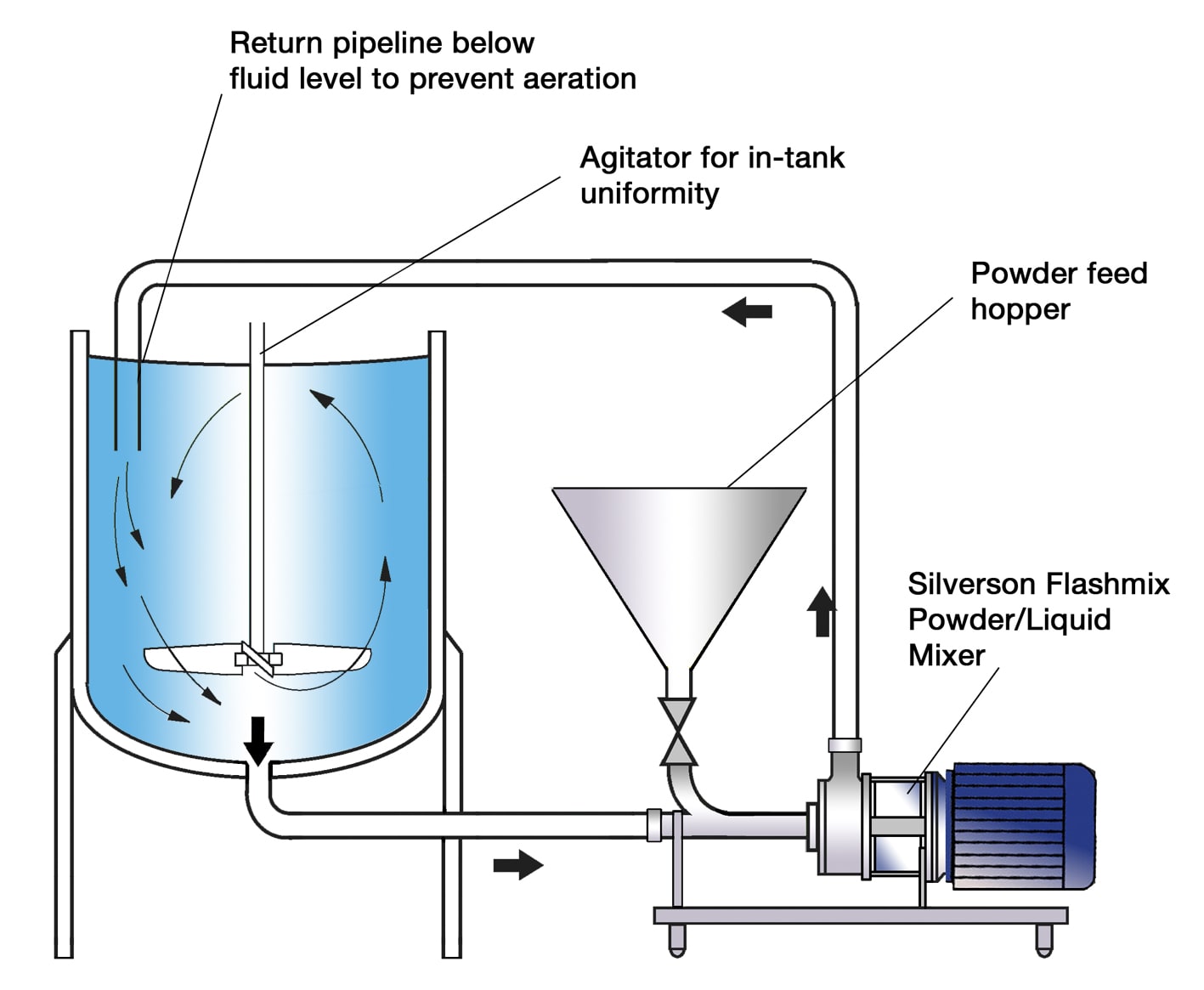
Silverson Flashmix
- Designed for rapid incorporation of large volumes of powder.
- Reduces aeration for improved mix quality.
- Requires minimal cleaning and operator input.
- Allows for controlled powder addition to prevent clumping.
- Suitable for high-viscosity and high-temperature applications.
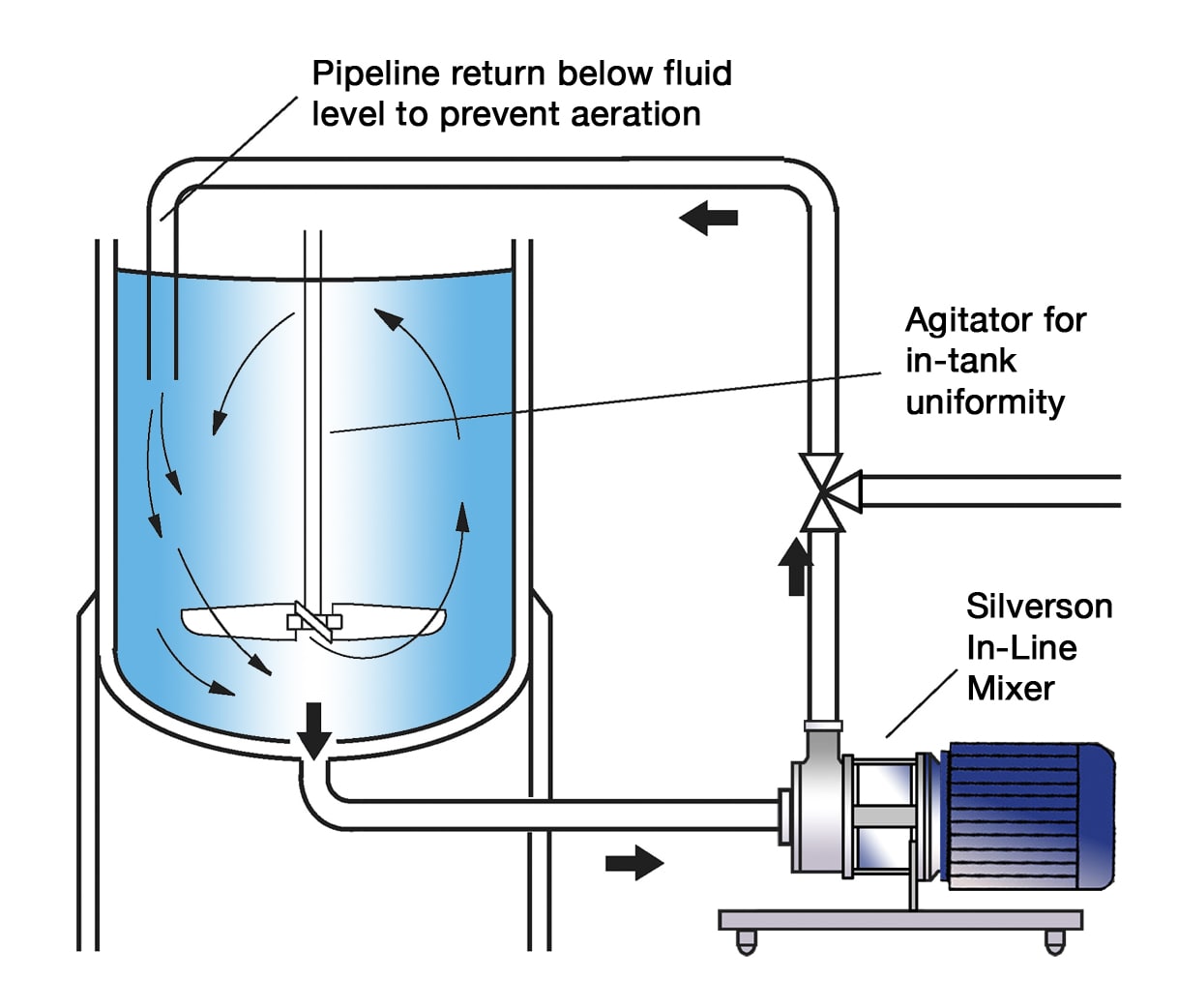
High Shear In-Line Mixers
- Ideal for large-scale production.
- Easily integrates with existing processing equipment.
- Provides aeration-free mixing with consistent results.
- Self-pumping capability can eliminate the need for additional transfer pumps.
- Can be used to discharge vessel.
- Available in ultra-sanitary and high-viscosity models.
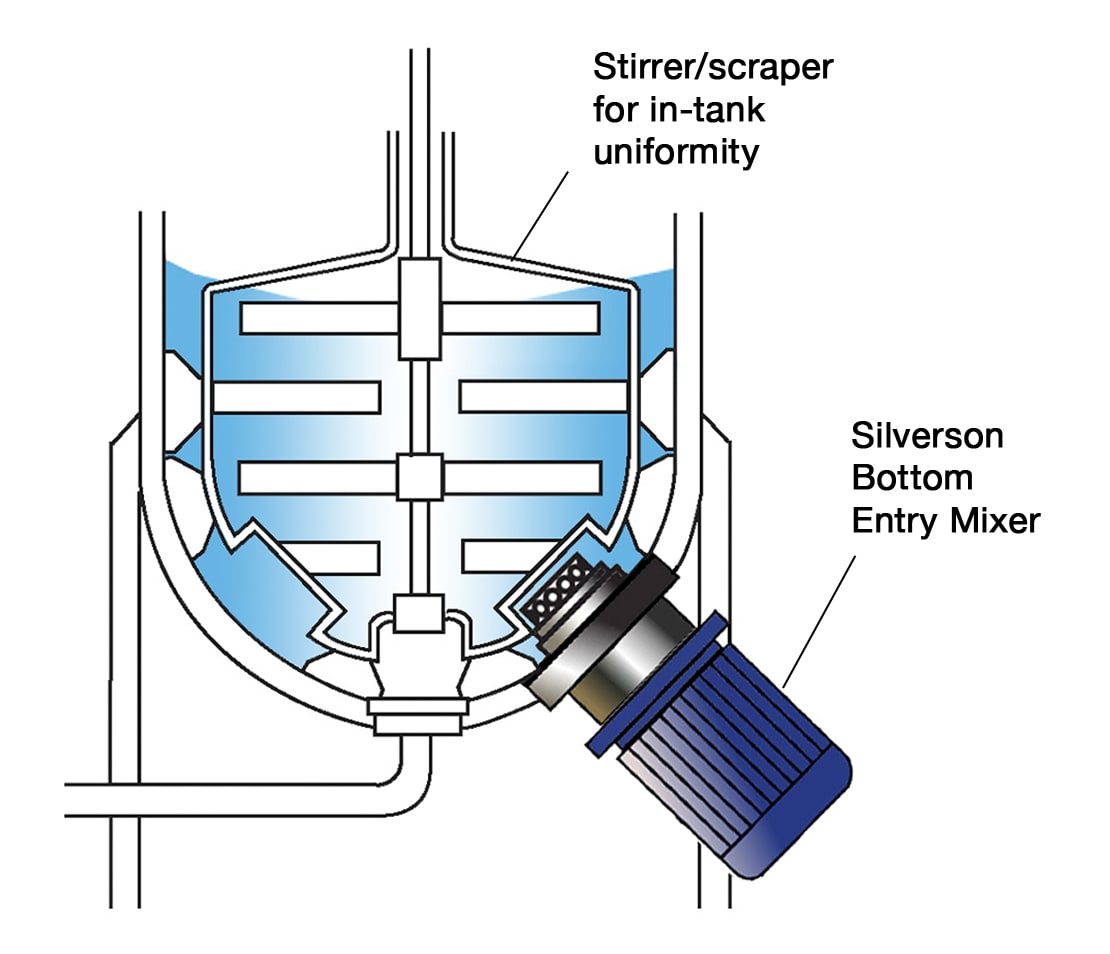
High Shear Bottom Entry Mixers
- Suitable for use on high viscosity products in conjunction with an anchor stirrer/scraper.
- No immersed shaft, reducing cleaning requirements.